Origin:

Flamegold (Koelreuteria elegans)
Native to Taiwan.
Naturalised Distribution:
Locally naturalised in south-eastern Queensland (e.g. around Brisbane and near Noosa) and in the coastal districts of north-eastern New South Wales (e.g. near Lismore).
Also naturalised in south-eastern USA (i.e. Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi and Florida) and on some Pacific islands (i.e. Hawaii and Guam).
Cultivation:
Golden rain tree (Koelreuteria elegans subsp. formosana) has been widely cultivated as a garden ornamental and street tree, particularly in the warmer parts of Australia.
Habitat:
A potential weed of roadsides, disturbed sites, waste areas, parks, urban bushland, riparian vegetation, gullies, forest margins and open woodlands in the sub-tropical, tropical and warmer temperate regions of Australia.
Distinguishing Features:
- A medium-sized tree usually growing 5-12 m tall.
- Its main trunk is covered in rough greyish-brown bark.
- Its twice-compound leaves are very large (25-60 cm long and 15-44 cm wide) and have numerous leaflets (5.5-10 cm long).
- Its large branched flower clusters (30-50 cm long) are borne at the tips of the branches in late spring or early summer.
- Its bright yellow flowers (up to 2 cm across) usually have four or five yellow petals and the same number of stamens.
- Its three-sided papery capsules pe (3.5-6 cm long) turn from bright red to pink and then eventually brown as they mature.
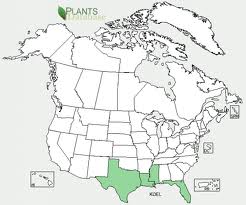
Flamegold (Koelreuteria elegans) Distribution in North America shown in green.
Habit:
A medium-sized tree usually growing 5-12 m tall, but capable of reaching up to 25 m in height.
Stems and Leaves:
The main trunk grows to about 50 cm across and is covered in rough greyish-brown bark that is furrowed lengthwise. Younger stems are pale brown or greenish in colour, finely hairy, and covered in small pale brown spots (i.e. lenticels).
The twice-compound (i.e. bipinnate) leaves are very large (25-60 cm long and 15-44 cm wide) and alternately arranged along the stems. These leaves are borne on stalks (i.e. petioles) and have several branches (i.e. pinnae), each carrying 8-17 leaflets (i.e. pinnules). The leaflets (5.5-10 cm long and 1.3-4 cm wide) are elongated to egg-shaped in outline (i.e. lanceolate to ovate) with entire to irregularly toothed (i.e. crenate or serrate) margins and long pointed tips (i.e. acuminate apices). They are mostly hairless (i.e. glabrous) or sparsely hairy (i.e. puberulent) and are either stalkless (i.e. sessile) or borne on tiny stalks (i.e. petiolules) up to 3 mm long.
Flowers and Fruit:
The large, branched, flower clusters (30-50 cm long and 20-25 cm wide) are borne at the tips of the branches (i.e. they are terminal panicles). These clusters contain numerous yellow flowers (up to 2 cm across) with four or five green sepals and four or five (rarely six) bright yellow petals

Close up of the Flamegold (Koelreuteria elegans) Weed.
(5.5-7 mm long and 1.5-3.5 mm wide). Each flower is borne on a short stalk (i.e. pedicel) and has the same number of stamens (4.5-10 mm long) as petals. Flowering occurs for a relatively brief period during late spring or early summer each year.
The inflated papery capsules are three-sided in nature and somewhat oval (i.e. ellipsoidal) in shape (3.5-6 cm long and 2.5-4.5 cm wide). These fruit are initially bright red to deep rose-purple, but fade gradually to pink and eventually brown in colour as they mature. Each capsule usually contains six seeds (5.2-5.5 mm across), two in each of its papery compartments. These seeds are rounded (i.e. globose) to pear-shaped (i.e. pyriform), black in colour, and either smooth or slightly rough in texture. The fruit are mostly present during late summer and autumn, but some may persist on trees into winter.
Reproduction and Dispersal :
Golden rain tree (Koelreuteria elegans subsp. formosana) reproduces by seed.
This species is generally spread to new areas by its deliberate cultivation. The seeds are blown from the trees still contained in their light and papery fruit (i.e. they are wind-dispersed) and may also be spread by water. They are probably also spread in dumped garden waste, while birds may also be a factor in their dispersal.
Impacts:
Golden rain tree (Koelreuteria elegans subsp. formosana) is regarded as an environmental weed in south-eastern Queensland and north-eastern New South Wales, and as a potential environmental weed in the Northern Territory and Western Australia. It is on the Alert List for Environmental Weeds, a list of 28 non-native plants that have the potential to seriously degrade Australia’s ecosystems.